The Origin of
Life

Prokaryotes were the first organisms to evolve. This would have occurred somewhere between 4.1 Ga, after
the Earth's crust began to solidify and 3.5 Ga, when the planet was inhabited
by bacteria that was advanced enough to build stromatolites. There
are various hypothesis's on the origin of life, taking into account the
few factors that we know about ancient earth (little oxygen, volcanic activity,
asteroids, ultraviolet radiation...) One hypothesis states that the
first organisms were the products of a chemical evolution that took place
in four stages;
-
the abiotic synthesis and accumulation of small organic molecules
or monomers, such as amino acids and nucleotides
-
the joining of these monomers into polymers, including proteins
and muclies acids
-
the aggregation of abiotically produced molecules into droplets
called protobionts, that had chemical characteristics different from their
surroundings;
-
the origin of heredity
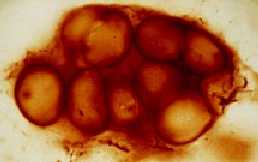
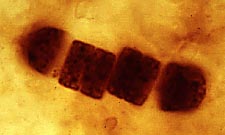
Ancient Fossil Bacteria : Pictured above are two kinds cyanobacteria
from the Bitter Springs chert of
central Australia, a site dating to the Late Proterozoic,
about 850 million years old. On the left is a
colonial chroococcalean form, and on the right
is the filamentous Palaeolyngbya. (www.ucmp.berkley.edu)